Rock types and rock cycle webquest – Embark on a captivating journey into the fascinating world of rock types and the dynamic rock cycle. This comprehensive webquest unveils the secrets of Earth’s rocky foundation, delving into the processes that shape our planet’s geological history.
Prepare to uncover the diverse characteristics of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, tracing their origins and exploring the forces that transform them. Discover the intricate interplay between plate tectonics and the rock cycle, unlocking the secrets of Earth’s ever-changing crust.
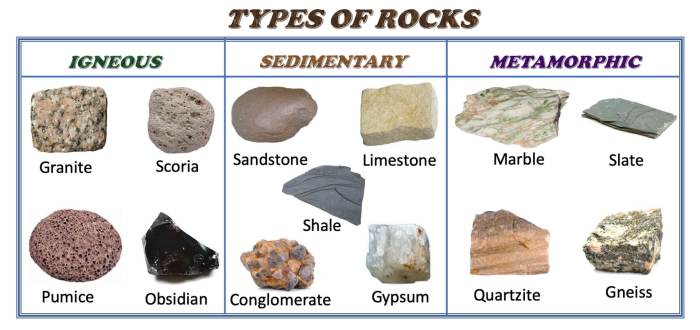
Rock Types
Rocks are solid, naturally occurring, inorganic substances that form the Earth’s crust. They are classified into three main categories based on their mode of formation: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
Igneous Rocks
- Formed from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma or lava).
- Examples: granite, basalt, pumice.
- Characteristics: crystalline texture, formed deep within the Earth’s crust or on the surface.
Sedimentary Rocks
- Formed from the accumulation and compaction of sediments (e.g., sand, clay, organic matter).
- Examples: sandstone, limestone, shale.
- Characteristics: layered or foliated texture, formed in water bodies or on land.
Metamorphic Rocks, Rock types and rock cycle webquest
- Formed when existing rocks are subjected to intense heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
- Examples: marble, slate, gneiss.
- Characteristics: foliated or non-foliated texture, formed deep within the Earth’s crust.
The type of rock formed depends on factors such as temperature, pressure, chemical composition, and the presence of water.
Rock Cycle
The rock cycle is a continuous process that describes the transformation of rocks from one type to another. It involves three main stages:
Diagram of the Rock Cycle
[Diagram yang menunjukkan tahapan rock cycle, termasuk proses yang terlibat]
Processes Involved
- Igneous to Sedimentary:Igneous rocks weather and erode, forming sediments that accumulate and compact into sedimentary rocks.
- Sedimentary to Metamorphic:Sedimentary rocks are subjected to heat and pressure, transforming them into metamorphic rocks.
- Metamorphic to Igneous:Metamorphic rocks can melt and recrystallize, forming igneous rocks.
Plate tectonics plays a crucial role in the rock cycle by facilitating the movement of rocks through different environments, subjecting them to various processes.
Rock Properties
Rocks have distinct physical and chemical properties that help identify and classify them.
Physical Properties
- Hardness:Resistance to scratching.
- Density:Mass per unit volume.
- Texture:Size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains.
These properties are useful for field identification and can provide insights into the rock’s origin and history.
Chemical Composition
Rocks are composed of minerals, each with its unique chemical composition. The presence and abundance of certain minerals can influence the rock’s overall properties and uses.
Rock Classification
Rocks are classified into various categories based on their composition, texture, and mode of formation.
Systems of Classification
- Igneous Rock Classification:Based on texture, composition, and origin (intrusive or extrusive).
- Sedimentary Rock Classification:Based on grain size, composition, and depositional environment.
- Metamorphic Rock Classification:Based on texture, mineralogy, and metamorphic grade.
Each system uses specific criteria to assign rocks to different classes, facilitating their identification and study.
Rock Uses
Rocks are widely used in human society for various purposes.
- Building Materials:Granite, marble, limestone.
- Road Construction:Basalt, sandstone.
- Jewelry:Diamonds, rubies, sapphires.
- Industrial Minerals:Quartz, feldspar, gypsum.
- Fuel Sources:Coal, natural gas.
The extraction and use of rocks have significant economic and environmental implications.
Rock Formation
Igneous Rock Formation
- Intrusive Igneous Rocks:Formed from magma that cools and solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface (e.g., granite).
- Extrusive Igneous Rocks:Formed from lava that cools and solidifies on the Earth’s surface (e.g., basalt).
Factors influencing igneous rock formation include temperature, pressure, cooling rate, and chemical composition.
Rock Weathering
Rock weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces and altering their composition.
Types of Weathering
- Physical Weathering:Mechanical breakdown of rocks due to temperature changes, frost action, and abrasion.
- Chemical Weathering:Alteration of rock minerals by water, oxygen, and acids.
Weathering products include soil, sediments, and dissolved ions.
Rock Identification
Identifying rocks involves examining their physical and chemical properties.
Key Features to Look For
- Color:Determined by mineral composition.
- Texture:Size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains.
- Hardness:Resistance to scratching.
- Luster:Way light interacts with the rock surface.
- Chemical Composition:Can be determined through laboratory analysis.
Using multiple methods ensures accurate rock identification.
Rock Exploration
Rock exploration involves searching for and assessing the availability of rocks and minerals.
Methods of Exploration
- Geological Mapping:Creating maps of rock formations.
- Geophysical Surveys:Using instruments to detect rocks and minerals beneath the surface.
- Drilling:Collecting rock samples for analysis.
Exploration is crucial for resource management and understanding the Earth’s geological processes.
Rock Conservation: Rock Types And Rock Cycle Webquest
Conserving rocks and minerals is essential for sustainable resource management.
Importance of Conservation
- Preservation of Geological Heritage:Rocks record Earth’s history and geological processes.
- Sustainable Resource Use:Ensuring the availability of rocks and minerals for future generations.
- Protection of Ecosystems:Rocks and minerals support diverse ecosystems.
Methods of Conservation
- Responsible Mining Practices:Minimizing environmental impacts.
- Land Use Planning:Designating areas for rock extraction and conservation.
- Public Education:Raising awareness about the importance of rock conservation.
FAQ Corner
What are the three main types of rocks?
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
How does plate tectonics influence the rock cycle?
Plate tectonics drives the movement of Earth’s crust, facilitating the processes of rock formation, transformation, and recycling.
What is the significance of rock classification?
Rock classification provides a systematic framework for understanding the diversity of rocks, aiding in their identification, study, and application.