Independent practice topographic maps answer key: a comprehensive guide to deciphering the intricate language of topographic maps. Join us as we embark on a journey to unlock the secrets of terrain, unraveling the mysteries hidden within the contours and symbols that define our landscapes.
Topographic maps, with their wealth of information, provide a detailed portrait of the Earth’s surface. They serve as indispensable tools for hikers, geologists, engineers, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the natural world. Our answer key empowers you to master the art of map interpretation, enabling you to extract valuable insights from these invaluable resources.
Independent Practice Topographic Maps
Independent practice topographic maps are maps designed specifically for individual practice and learning. They are typically used by students, hikers, and other outdoor enthusiasts to develop their map-reading skills.
Independent practice topographic maps provide a safe and controlled environment for individuals to learn how to interpret topographic maps and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios. They offer a variety of features and exercises that guide users through the process of map reading, from basic concepts to more advanced techniques.
Map Features and Symbols
Topographic maps use a variety of features and symbols to represent terrain features and other geographic information. These features include:
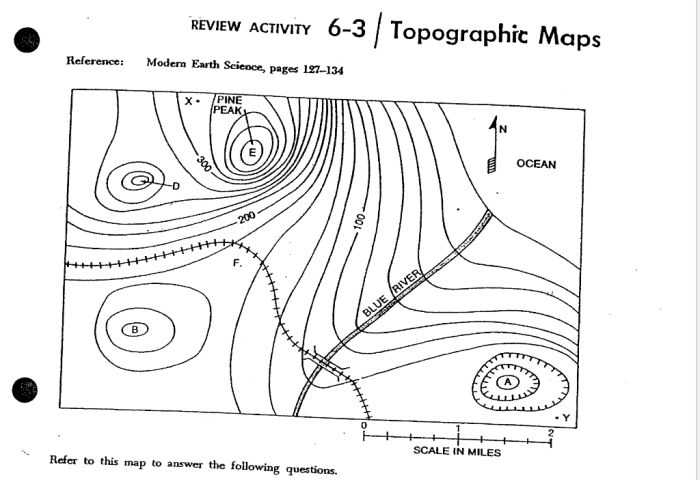
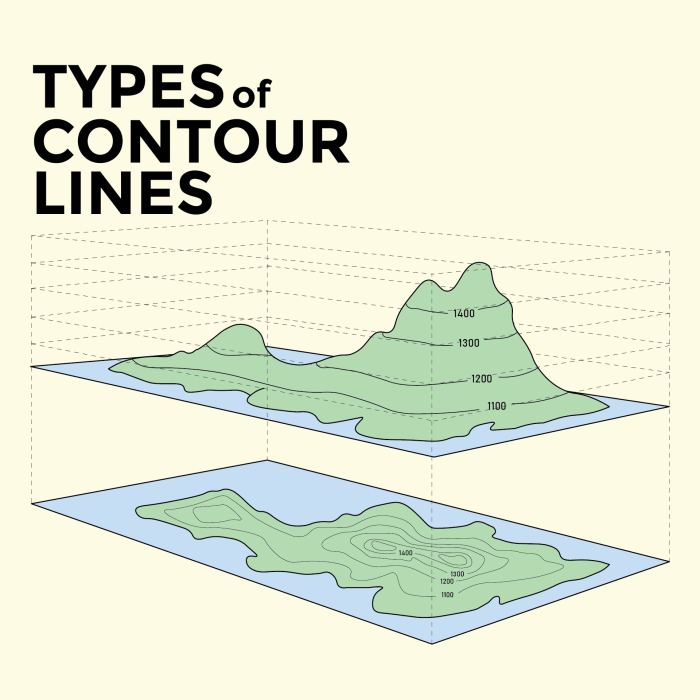
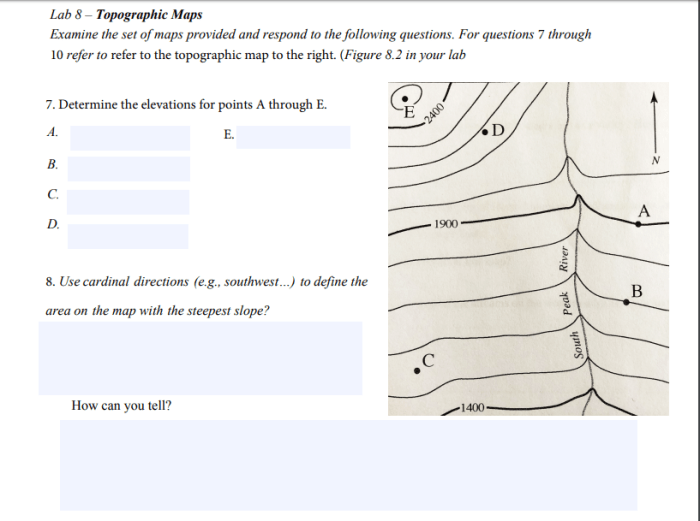
- Contour lines:Lines that connect points of equal elevation, providing a detailed representation of the terrain.
- Spot elevations:Points with their elevation marked, used to supplement contour lines and provide more precise elevation information.
- Map symbols:Standardized symbols that represent various features, such as roads, buildings, and water bodies.
- Scale:A ratio that indicates the relationship between the map and the actual terrain.
- North arrow:Indicates the direction of true north.
Contour Lines, Independent practice topographic maps answer key
Contour lines are one of the most important features on topographic maps. They are lines that connect points of equal elevation, providing a detailed representation of the terrain.
By interpreting contour lines, users can determine the elevation, slope, and terrain features of an area. For example, closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced contour lines indicate gentle slopes.
Map Scales and Distances
The scale of a topographic map is the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
Understanding map scales is essential for determining distances on a map. For example, a map with a scale of 1:24,000 means that one inch on the map represents 24,000 inches (or 2,000 feet) on the ground.
Map Projections
Map projections are mathematical formulas that transform the curved surface of the Earth into a flat map.
There are many different types of map projections, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common map projection used for topographic maps is the Mercator projection, which is a cylindrical projection that preserves the shape of landmasses but distorts their size and distance.
Applications of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have a wide range of applications in fields such as:
- Geology:Identifying and mapping geological features, such as faults and folds.
- Engineering:Planning and designing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure.
- Land use planning:Identifying suitable areas for development, conservation, and recreation.
- Navigation:Helping hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts find their way in unfamiliar terrain.
FAQ Corner: Independent Practice Topographic Maps Answer Key
What are the key features of topographic maps?
Topographic maps are characterized by their use of contour lines to depict elevation, along with symbols and annotations that represent various natural and man-made features, such as rivers, roads, and vegetation.
How do I determine the elevation of a point on a topographic map?
Locate the point on the map and identify the nearest contour line. The elevation of the point is indicated by the elevation value printed next to the contour line.
What is the purpose of map scales?
Map scales provide a ratio that relates the distance on the map to the corresponding distance on the ground. They enable users to determine the actual distances between points on the map.