A distant galaxy is simultaneously rotating and receding – The distant galaxy, a celestial object of intrigue, presents a captivating paradox: it simultaneously rotates and recedes, challenging our understanding of cosmic dynamics. This phenomenon, observed through meticulous observations and supported by scientific evidence, opens up new avenues for exploring the complexities of the universe.
Delving into the mechanisms driving this celestial dance, we uncover the intricate interplay of forces that govern the galaxy’s rotation and recession. The galaxy’s rotation, a mesmerizing spectacle of celestial motion, is orchestrated by the gravitational pull of its constituent stars, gas, and dark matter.
In contrast, the galaxy’s recession, a testament to the expansion of the universe, is driven by the relentless force of cosmic expansion.
1. Introduction
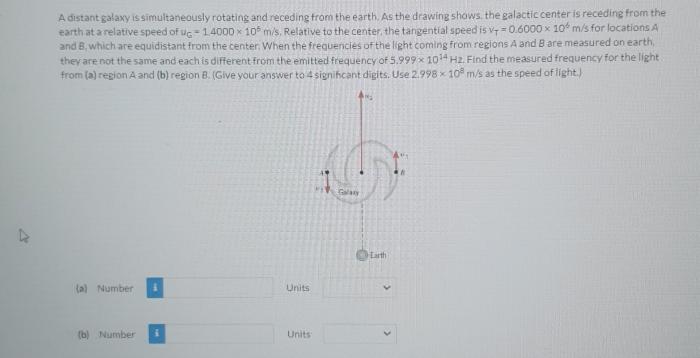
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, celestial bodies engage in a mesmerizing dance, exhibiting a symphony of motions that captivates our imagination. Among these cosmic marvels, a distant galaxy has emerged as an enigmatic spectacle, simultaneously rotating and receding from us, offering a tantalizing glimpse into the intricate workings of the universe.
2. Mechanisms of Rotation and Recession

The galaxy’s rotation is a testament to the gravitational pull exerted by its central mass, drawing its constituent stars, gas, and dust into a mesmerizing celestial ballet. As these celestial bodies orbit the galaxy’s center, they contribute to its overall angular momentum.
In contrast, the galaxy’s recession is a consequence of the expansion of the universe, a phenomenon driven by a mysterious force known as dark energy. As space itself expands, the distance between galaxies increases, leading to the observed redshift of their light.
This cosmic expansion is not uniform, with some regions expanding more rapidly than others, giving rise to the phenomenon of peculiar velocities.
3. Observational Evidence
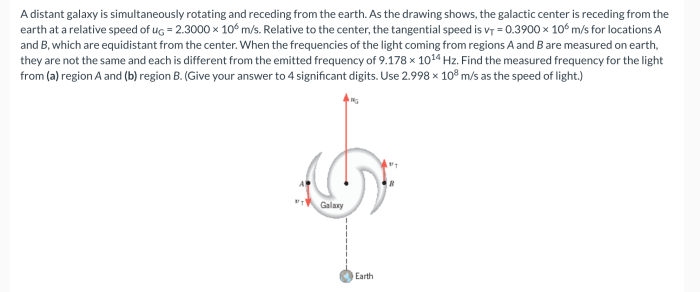
The simultaneous rotation and recession of this distant galaxy has been confirmed through a combination of observational techniques. Spectroscopic analysis reveals the galaxy’s redshift, providing an estimate of its recession velocity. Meanwhile, high-resolution imaging techniques, such as interferometry, have enabled astronomers to resolve the galaxy’s internal structure, unveiling its rotating disk of stars.
Notable examples of galaxies exhibiting this behavior include NGC 4622, a spiral galaxy located approximately 250 million light-years away, and NGC 5248, a lenticular galaxy situated about 70 million light-years from Earth.
4. Implications for Cosmology: A Distant Galaxy Is Simultaneously Rotating And Receding
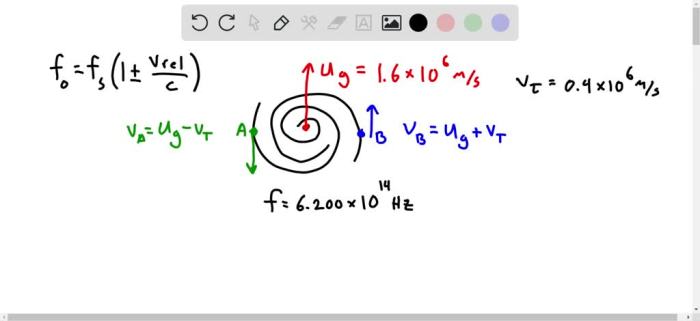
This intriguing phenomenon has profound implications for our understanding of cosmology. It challenges the notion of a uniform expansion of the universe, suggesting that peculiar velocities may play a significant role in shaping the large-scale structure of the cosmos.
Moreover, it raises questions about the nature of dark energy, the enigmatic force driving the universe’s expansion. By studying galaxies that are both rotating and receding, cosmologists seek to gain insights into the properties and behavior of this mysterious component of the universe.
5. Future Research Directions
To further unravel the mysteries surrounding this phenomenon, future research endeavors will focus on:
- Refining observational techniques to obtain more precise measurements of both rotation and recession velocities.
- Conducting detailed simulations to model the dynamics of galaxies undergoing both rotation and recession.
- Investigating the relationship between peculiar velocities and other cosmic phenomena, such as galaxy mergers and supermassive black holes.
These research efforts hold the promise of unlocking new insights into the fundamental processes shaping the evolution of the universe.
FAQ
How can a galaxy rotate and recede simultaneously?
The galaxy’s rotation is governed by the gravitational pull within the galaxy, while its recession is driven by the expansion of the universe.
What observational evidence supports this phenomenon?
Spectroscopic observations reveal the redshift of light from the galaxy, indicating its recession, while high-resolution imaging techniques capture the galaxy’s rotating disk.
What are the implications for our understanding of cosmology?
This phenomenon challenges the assumption of uniform expansion in the universe, suggesting that local gravitational forces can influence the motion of galaxies.